

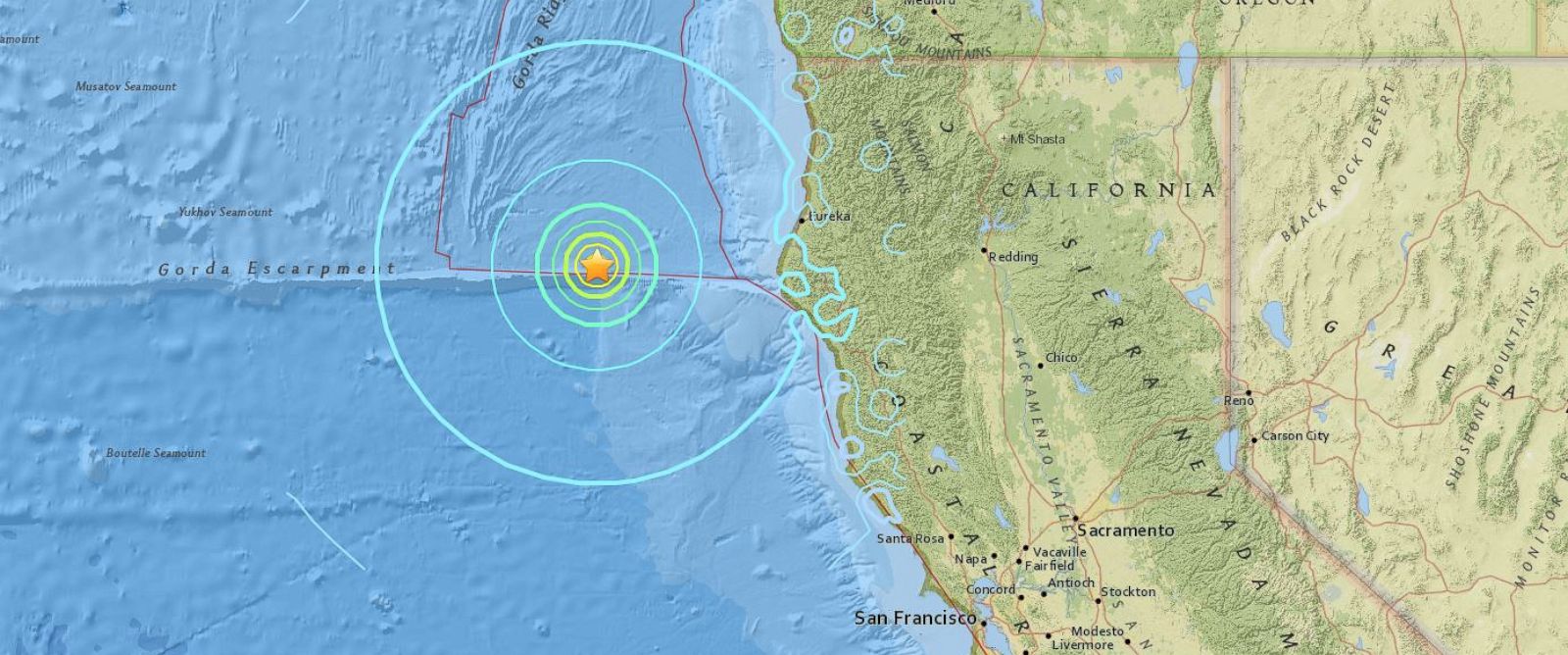
Neither earthquake struck along the San Andreas Fault, officials said. Thursday’s earthquake was felt in central Los Angeles as a long, rolling quake, making buildings rock back and forth for at least several seconds, but there were few reports of damage in the city. People in most of Southern California as well as parts of Arizona and Nevada reported feeling the tremor, but the location was “so remote that it caused relatively negligible damage,” the Southern California Earthquake Data Center said. The Hector Mine earthquake struck in the early morning hours of October 16, 1999. The 6.4 magnitude quake that struck Thursday near the town of Ridgecrest – a community west of the Mojave Desert – was felt in Los Angeles and Las Vegas. The driving force of earthquakes in California is movement along the San Andreas Fault and the many associated faults within the San Andreas Fault System that. But even a 7-magnitude quake would be smaller, and obviously, cause damage to structures that are already damaged and vulnerable.The last time Southern California saw such a large earthquake was nearly 20 years ago, when the magnitude 7.1 Hector Mine quake, centered in a remote part of the Mojave Desert, shook the region. Typically, aftershocks are smaller than the initial, main shock which was a 7.6 in this case. Aftershocks will continue there for years, and some of those could potentially be damaging. What happened last week has changed the stress in the surrounding areas closer to Mexico that directly impact the faults.
Ghosh: Mexico sits on what we call a subduction zone, which is prone to large earthquakes. Q: Have the Mexican quakes made it less likely that they will experience another big shaker anytime soon? Have an earthquake kit ready and accessible at all times, in your car, home and workplace. Drop, cover, and hold on when you feel the shaking. Therefore, it is always a good idea to be prepared for that. When the San Andreas goes, it will definitely produce a similar magnitude event, like the Mexican ones. Northern California has had: (M1.5 or greater) 11 earthquakes in the past 24 hours. These can and will produce damaging earthquakes in the future. Ghosh: Southern California hosts a large fault, the San Andreas fault, as well as others, like the San Jacinto fault. Q: What is the likelihood of an earthquake in this region even without the recent Mexican events? It is only a matter of time before we are subject to the same kind of shaking and damage. Mexico’s recent earthquakes may not have significantly changed the stress on our faults, but it’s a good reminder of what can happen here. These are typically smaller earthquakes, but not always. As they do, they can trigger earthquakes anywhere. With dynamic triggers, seismic waves produced by one earthquake propagate remotely through the entire Earth.
The other way, dynamic triggering, can work remotely. One is a static trigger, when moving rocks upset a fault that is only one or two hundred kilometers away from the original fault. There are two ways one large seismic event can trigger another. In rare cases, such waves from distant quakes may trigger more damaging events, but again, it is not very common. However, the seismic waves generated by the large earthquake have propagated through our region and shaken the ground, and that may trigger smaller earthquakes. Ghosh: Because the earthquake in Mexico was about 1,300 miles away from Southern California, there is no direct impact on local faults. A magnitude 6.0 (M6. By Communications and Publishing July 8, 2021. On Thursday, a 6.4 magnitude earthquake struck the area. The USGS has up-to-date details on the Jevent. Abhijit Ghosh conducting fieldwork in the Mojave Desert with a seismic station. A pair of large earthquakes hit Southern California over the course of two days.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
